There will be attenuation losses in the fiber when the signals transmit over long distances. To compensate for the attenuation losses, optical amplifier which could restore the optical signal to its original power level without E-O and O-E (electrical to optical and optical to electrical) conversions is needed. Optical amplifier is an important enabling technology for optical communication networks. There are three common optical amplifiers which include erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA), the semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), and the Raman amplifier. Among them EDFA is most often applied in optical communications.
Definition
EDFA uses a short length of optical fiber doped with the rare-earth element erbium that has the appropriate energy levels in the atomic structures for amplifying optical signal. It’s designed to amplify light at wavelengths around 1550 nm and make wavelengths suffer minimum attenuation in optical fibers. EDFA often uses a 980nm or 1480nm pump laser to inject energy into the doped fiber. The 980nm band has a higher absorption cross-section and is generally used for low-noise performance. The 1480nm band has a lower but broader absorption cross-section and is generally used for high power amplifiers.
Principle of EDFA
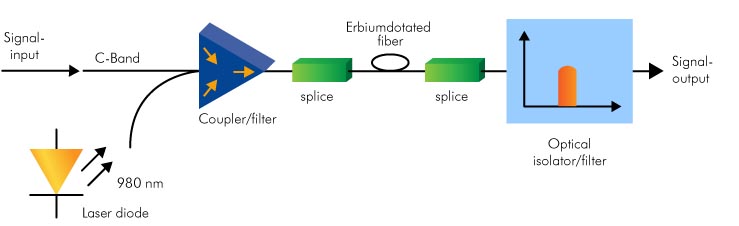
The principle of EDFA is shown as the following picture. EDFA usually consists of a length of EDF (erbium-doped fiber), a pump laser, and a component (often known as a WDM coupler) for combining the signal and pump wavelength and an isolator. The pump laser, known as pumping bands, inserts dopants into the silica fiber and makes erbium enter into an excited state. When the weak signals at 1310 nm or 1550 nm travel through the fiber, the lights will stimulate the excited atoms of erbium so that the atoms can release energy in the form of photons. The emitted light photons which have the same wavelength with input signals amplify the optical signals. The signals passing by the fiber will grow stronger and stronger. And the function of the isolator usually placed at the output is to prevent reflections returning from the attached fiber. Because the reflections can disrupt amplifier operation. Thus, EDFA is a high gain amplifier.
Applications
EDFA has many useful functions in telecom systems for fiber communications. For instance, it can boost the power of a data transmitter before entering a long fiber span. It could also be used in front of a data receiver if the arriving signal is weak. What’s more, an EDFA can be used to maintain extended spans of passive transmission fiber. So that the transmission losses through the long distance fiber could be compensated. EDFA is oftern applied in DWDM, CATV, SDH. In addition, an EDFA could be used as the equipment for testing transmission hardware.
Conclusion
In long distance communications, the signals should be amplified to avoid the attenuation losses. There are many kinds of optical amplifiers could be used to amplify the signal but some of them are not very often applied because of certain obvious disadvantages. For example, SOA will add noise to the signal. While EDFA has some interesting properties for fiber optics communications due to its rare-earth element. EDFA is a low-noise amplifier which can simultaneously amplify many data channels at different wavelengths with flat gain, high saturation output power and stable operation. So these advantages make EDFA the most popular in optical communication applications.
Originally published at http://www.china-cable-suppliers.com/
No comments:
Post a Comment