The demand for high bandwidth promotes the development of data transmission technology. Ethernet standard continuously evolves to meet fast speed need, from 100BASE, 1000BASE to 10GBASE. Meanwhile, the data carrying technology also develops to provide great bandwidth for transporting data with low cost, such as the copper and fiber cables as well as optical transceiver modules.
 Figure1. 10G Structured Cabling
Figure1. 10G Structured Cabling
Copper and Fiber
In 10 Gigabit Ethernet, copper and fiber are used to transport data. Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Copper is more affordable and easy to install. It acts the best when used in short lengths, typically 100 meters or less. But when deployed over long distance, electromagnetic signal characteristics will influence its performance. Besides, bundling copper cabling can cause interference, which makes it difficult to employ as a comprehensive backbone. So copper cabling are widely used in PCs and LANs communication network instead of campus or long-distance transmission.
Compared with copper, fiber cabling is usually used for long distance communication among campus, and environments that need protection from interference, such as manufacturing areas. In addition, fiber cabling is more reliable and less susceptible to attenuation, which makes it suitable for data transmission distance over 100 meters. But fiber still has drawbacks. It’s more costly than copper.
The Evolution of Cabling Technologies
Since 10 GbE technologies have changed, so have the cabling technologies. There are two main standards: IEEE802.3ae and IEEE802.3ak. Factors covered in these standards like transmission distance and equipment being used are helpful to determine the cabling strategy.
- IEEE802.3ae
IEEE802.3ae standard updates the existing IEEE802.3 standard for 10GbE fiber transmission. The new standard defines several new media types for LAN, metropolitan area network (MAN) and wide area network (WAN) connectivity.
10GBASE-SR – it supports 10GbE transmission over standard multimode fiber (850 nm) for distances of 33 and 86 meters. The SR standard also supports up to 300 meters using the new 2000MHz/km multimode fiber (laser optimized). This one is the lowest-cost optics for 10GbE.
10GBASE-LR – it uses optics (1310nm) and supports single-mode fiber up to 10 km.
10GBASE-LX4 – it can support multimode fiber for distances up to 300 meters using Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM). The LX4 standard also supports single-mode fiber for up to 10 Km. LX4 is more expensive than both SR and LR because it requires four times the optical and electrical circuitry in addition to optical multiplexers.
10GBASE-ER – it uses optics (1550nm) to support single-mode fiber up to 30 km.
- IEEE802.3ak / 10GBASE-T
10GBASE-T is the latest proposed 10GbE standard for use with unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) style cabling. This standard is to improve the performance and increase the transmission distance at a lower cost. Category 5 (Cat 5) and Category 6 (Cat 6) are the most common cabling systems being installed today. But Cat 5 can’t meet the bandwidth demands of 10GbE’s transmission. To meet the needs of 10GbE, manufacturers create Category 6A (Cat 6A), designed with existing Cat 6 cable but measured and specified to higher frequencies. In addition to Cat 6A, 10GBASE-T will operate on Category 7 (Cat 7) cables.
10GbE Transceivers
Except the cabling, transceivers also need to be considered for the network connectivity. Transceivers provide the interface between the equipment sending and receiving data. 10GbE has four defined transceiver types, including XENPAK, X2, XFP and SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus). These transceivers are pluggable and are compliant with 802.3ae standard.
Among them, SFP+ is the smallest 10G form factor. And it can interoperate with XENPAK, X2, XFP interface on the same link. Fiberstore provides a number of interfaces attempted to satisfy different objectives including support for MMF and SMF compatibility, such as SFP-10G-SR, SFP-10G-LR, SFP-10G-ER, SFP-10G-ZR, etc. For example, SFP-10G-SR transceiver module can support 300 meters data transmission distance over 850 nm multimode fiber. And SFP-10G-LR module supports the link length up to 10 kilometers over 1310 nm single mode fiber.
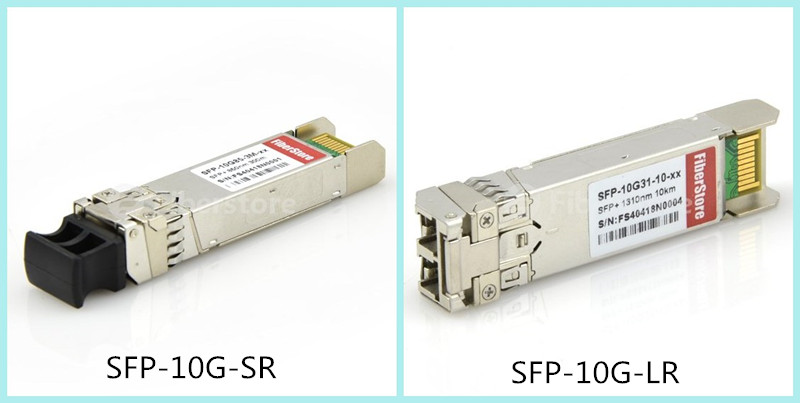
Figure2. SFP+ Transceiver
As the corresponding cabling technology gets great improvement, 10G network is becoming more affordable and pervasive. 10G network brings us higher speed. For 10G network connectivity, SFP+ transceivers are recommended to transport data over copper or fiber cabling.
Originally published at www.fiber-optic-equipment.com
No comments:
Post a Comment