Data transmission through fiber optic cable has many advantages over other transmission media such as copper cable or radio. Compared with other transmission media, fiber optic cable is lighter, smaller and more flexible with faster speed over long distance. However, there are some factors influencing the performance of fiber optic cable. Fiber optic loss is an important factor to be considered when selecting and installing cables. This article will introduce detailed information about fiber optic loss.
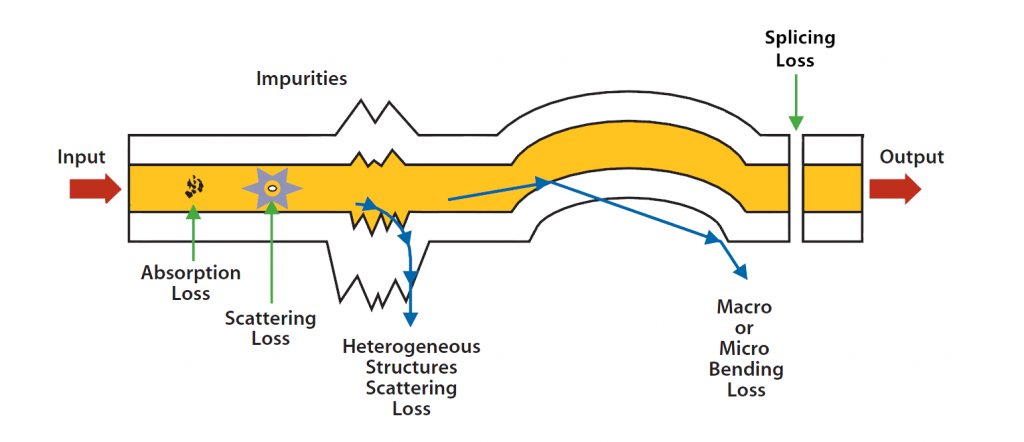
When a beam of light carrying signals travels through the core of fiber optic cable, the light will become weaker. That means the signals will be weaker. This phenomenon is called fiber optic loss or attenuation. The decrease in power level is described in dB. To transmit optical signals smoothly and safely, fiber optic loss must be decreased. Fiber optic loss is caused by internal reasons and external causes, which are also known as intrinsic fiber core attenuation and extrinsic fiber attenuation.
Intrinsic Fiber Core Attenuation
Internal fiber optic loss, also usually called intrinsic attenuation, is caused by the fiber optic cable itself. There are two causes of intrinsic attenuation. One is light absorption and the other one is scattering.
Light absorption is a major reason of fiber optic loss during optical transmission. Light is absorbed in the fiber by the materials of fiber optic cable. So light absorption is also known as material absorption. The lost power actually transferred into other forms of energy like heat because of molecular resonance and wavelength impurities. Atomic structure lies in any pure material and they absorb selective wavelengths of radiation. More over, we can’t find total pure materials in the market. So manufacturers use germanium and other materials with pure silica to optimize the fiber optic core performance.
The scattering of light is caused by molecular level irregularities in the glass structure. The light scatters in all direction. Some of them keeps traveling in the forward direction. And the light not scattered in the forward direction will be lost in the fiber optic link. Thus, to reduce fiber optic loss caused by scattering, the fiber optic core should be almost perfect and the fiber optic coating and extrusion should be carefully controlled.
Extrinsic Fiber Attenuation
Extrinsic fiber attenuation is also an important factor influencing the performance of fiber optic cable. It’s usually caused by improper handling of fiber optic cable including bend loss and splicing loss.
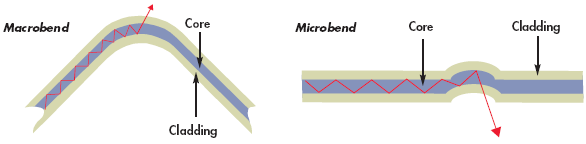
Bend loss is generally caused by fiber optic bend. There are two kinds of bending: micro bending and macro bending. Macro bending refers to a large bend in the fiber (with more than a 2 mm radius). To reduce fiber optic loss, you should better notice the followings:
- Fiber core deviate from the axis;
- Manufacturing defects;
- Mechanical constraints during the fiber laying process;
- Environmental variations like the change of temperature, humidity or pressure.
Fiber optic splicing is another cause of extrinsic fiber attenuation. It’s very common to splice fiber optic cable. So the splicing loss can’t be avoided but can be reduced with proper handling ways. For example, you can choose high quality fiber optic connectors and fusion splicing machine.
There are many factors causing fiber optic loss. To reduce the intrinsic fiber core attenuation, you should select good quality fiber optic cable. To reduce extrinsic fiber attenuation, you should better need proper handling and skills.
Originally published at www.fiber-optic-equipment.com
No comments:
Post a Comment